
We are pleased to share with you the 50 most downloaded Nature Communications articles* in the life and biological sciences published in 2020. (Please note we have a separate collection on the Top 50 SARS-CoV-2 papers.) Featuring authors from around the world, these papers highlight valuable research from an international community.
Browse all Top 50 subject area collections here.
* Data obtained from SN Insights (based on Digital Science's Dimensions) and has been normalised to account for articles published later in the year.

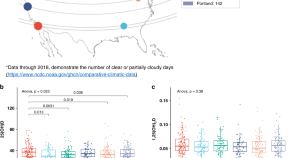
Here, the authors investigate associations of vitamin D metabolites with gut microbiome in a cross-sectional analysis of 567 elderly men enrolled in the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) Study and find larger alpha-diversity correlates with high 1,25(OH)2D and high 24,25(OH)2D and higher ratios of activation and catabolism.

The accurate representation of data is essential in science communication, however, colour maps that visually distort data through uneven colour gradients or are unreadable to those with colour vision deficiency remain prevalent. Here, the authors present a simple guide for the scientific use of colour and highlight ways for the scientific community to identify and prevent the misuse of colour in science.
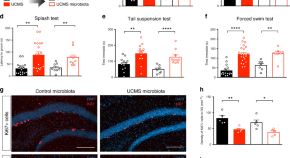
The gut microbiota may contribute to depression, but the underlying mechanism is not well understood. Here the authors use a mouse model of stress induced depression to demonstrate that behavioural changes conferred by fecal transplant from stressed to naïve mice require the endocannabinoid system.
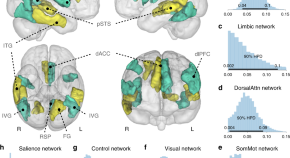
Here, using pattern-learning analyses of structural, functional, and diffusion brain scans in ~40,000 UK Biobank participants, the authors provide population-scale evidence that the default network is associated with perceived social isolation.
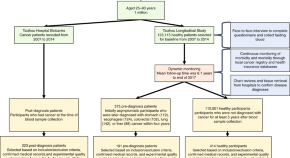
Patients whose disease is diagnosed in its early stages have better outcomes. In this study, the authors develop a non invasive blood test based on circulating tumor DNA methylation that can potentially detect cancer occurrence even in asymptomatic patients.
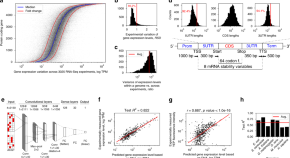
Regulatory and coding regions of genes are shaped by evolution to control expression levels. Here, the authors use deep learning to identify rules controlling gene expression levels and suggest that all parts of the gene regulatory structure interact in this.
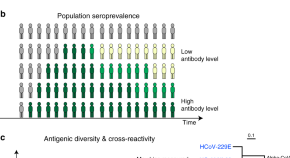
Antibody mediated immunity to SARS-CoV-2 will affect future transmission and disease severity. This systematic review on antibody response to coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and endemic coronaviruses provides insights into kinetics, correlates of protection, and association with disease severity.
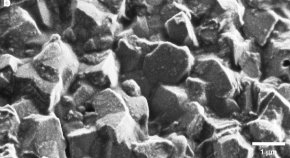
Biomineral armour is known in a number of diverse creatures but has not previously been observed in insects. Here, the authors report on the discovery and characterization of high-magnesium calcite armour which overlays the exoskeletons of leaf-cutter ants.
Organ transplantation involving aged donors is often confounded by reduced post-transplantation organ survival. By studying both human organs and mouse transplantation models, here the authors show that pretreating the donors with senolytics to reduce mitochondria DNA and pro-inflammatory dendritic cells may help promote survival of aged organs.
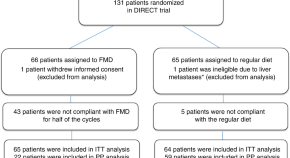
Preclinical evidence suggests that a fasting mimicking diet (FMD) can make cancer cells more vulnerable to chemotherapy, while protecting normal cells. In this randomized phase II clinical trial of 131 patients with HER2 negative early stage breast cancer, the authors demonstrate that FMD is safe and enhances the effects of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on radiological and pathological tumor response.
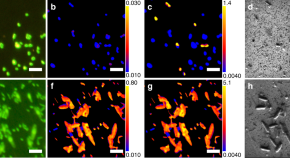
The discovery of aerobic microbial communities in nutrient-poor sediments below the seafloor begs the question of the mechanisms for their persistence. Here the authors investigate subseafloor sediment in the South Pacific Gyre abyssal plain, showing that aerobic microbial life can be revived and retain metabolic potential even from 101.5 Ma-old sediment.
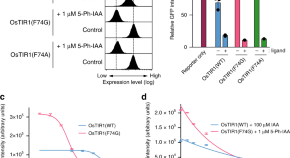
Auxin-inducible degron systems can be leaky and require high doses of auxin. Here the authors establish AID2 which uses an OsTIR1 mutant and the ligand 5-Ph-IAA to overcome these problems and establish AID-mediated target depletion in mice.
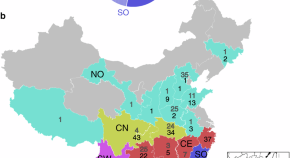
Bats are a likely reservoir of zoonotic coronaviruses (CoVs). Here, analyzing bat CoV sequences in China, the authors find that alpha-CoVs have switched hosts more frequently than betaCoVs, identify a bat family and genus that are highly involved in host-switching, and define hotspots of CoV evolutionary diversity.
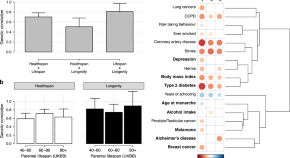
Ageing phenotypes are of great interest but are difficult to study genetically, partly due to the sample sizes required. Here, the authors present a multivariate framework to combine GWAS summary statistics and increase statistical power, identifying additional loci enriched for aging.
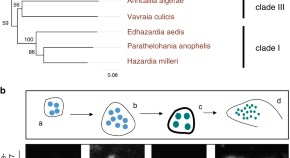
Mircobial symbionts of mosquitoes can affect transmission of human pathogens. Here, Herren et al. identify a microsporidian symbiont in Anopheles gambiae that impairs transmission without affecting mosquito fecundity or survival.
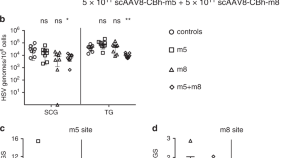
Herpes simplex virus establishes lifelong latency in ganglionic neurons, which are the source for recurrent infection. Here Aubert et al. report a promising antiviral therapy based on gene editing with adeno-associated virus-delivered meganucleases, which leads to a significant reduction in ganglionic HSV loads and HSV reactivation.
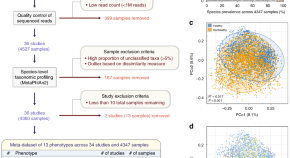
A biologically-interpretable and robust metric that provides insight into one’s health status from a gut microbiome sample is an important clinical goal in current human microbiome research. Herein, the authors introduce a species-level index that predicts the likelihood of having a disease.
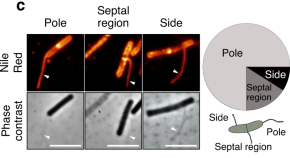
Bacterial nanotubes and other similar membranous structures have been reported to function as conduits between cells to exchange DNA, proteins, and nutrients. Here the authors provide evidence that bacterial nanotubes are formed only by dead or dying cells, thus questioning their previously proposed functions.
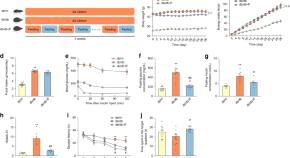
Intermittent fasting (IF) has been shown beneficial in reducing metabolic diseases. Here, using a multi-omics approach in a T2D mouse model, the authors report that IF alters the composition of the gut microbiota and improves metabolic phenotypes that correlate with cognitive behavior.
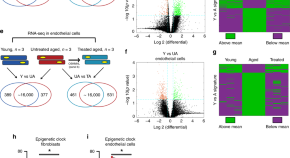
Aging involves gradual loss of tissue function, and transcription factor (TF) expression can ameliorate this in progeroid mice. Here the authors show that transient TF expression reverses age-associated epigenetic marks, inflammatory profiles and restores regenerative potential in naturally aged human cells.
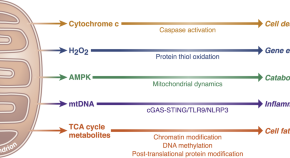
Mitochondrial metabolites contribute to more than biosynthesis, and it is clear that they influence multiple cellular functions in a variety of ways. Here, Martínez-Reyes and Chandel review key metabolites and describe their effects on processes involved in physiology and disease including chromatin dynamics, immunity, and hypoxia.
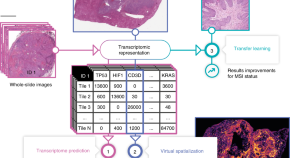
RNA-sequencing of tumour tissue can provide important diagnostic and prognostic information but this is costly and not routinely performed in all clinical settings. Here, the authors show that whole slide histology slides—part of routine care—can be used to predict RNA-sequencing data and thus reduce the need for additional analyses.
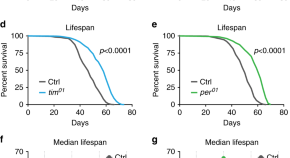
Disruption of different components of molecular circadian clocks has varying effects on health and lifespan of model organisms. Here the authors show that loss of period extends life in drosophila melanogaster.
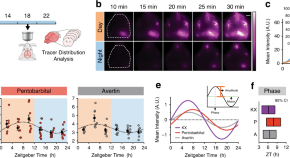
Glymphatic function is increased during the rest phase while more cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) drains directly to the lymphatic system during the active phase. The water channel aquaporin-4 supports these endogenous, circadian rhythms in CSF distribution.
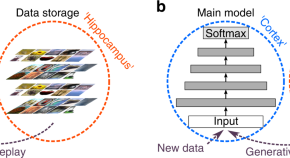
One challenge that faces artificial intelligence is the inability of deep neural networks to continuously learn new information without catastrophically forgetting what has been learnt before. To solve this problem, here the authors propose a replay-based algorithm for deep learning without the need to store data.
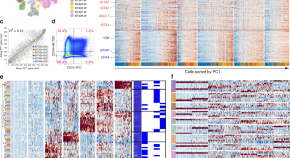
Glioblastoma is thought to arise from neural stem cells. Here, to investigate this, the authors use single-cell RNA-sequencing to compare glioblastoma to the fetal human brain, and find a similarity between glial progenitor cells and a subpopulation of glioblastoma cells.
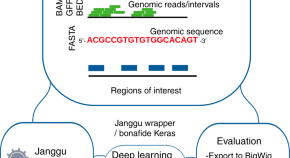
Deep learning is becoming a popular approach for understanding biological processes but can be hard to adapt to new questions. Here, the authors develop Janggu, a python library that aims to ease data acquisition and model evaluation and facilitate deep learning applications in genomics.
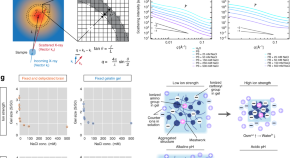
Tissue clearing has revolutionised histology, but limited penetration of antibodies and stains into thick tissue segments is still a bottleneck. Here, the authors characterise optically cleared tissue as an electrolyte gel and apply this knowledge to stain the entirety of thick tissue samples.
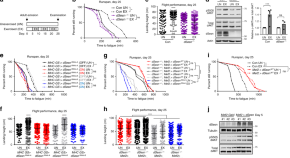
Exercise improves metabolic health and physical condition, particularly important for health in aged individuals. Here, the authors identify that Sestrins, proteins induced by exercise, are key mediators of the metabolic adaptation to exercise and increase endurance through the AKT and PGC1a axes.
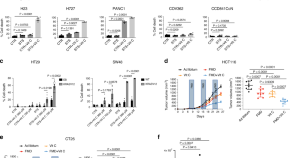
Fasting diets are emerging as an approach to delay tumor progression and improve cancer therapies. Here, the authors show that the combination of fasting-mimicking diet with vitamin C decreases tumor development and increases chemotherapy efficacy in KRAS-mutant cancer.
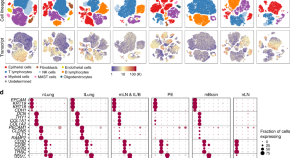
Understanding the mechanisms that lead to lung adenocarcinoma metastasis is important for identifying new therapeutics. Here, the authors document the changes in the transcriptome of human lung adenocarcinoma using single-cell sequencing and link cancer cell signatures to immune cell dynamics.
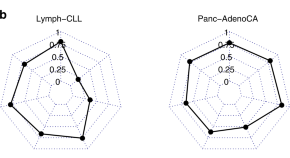
Some cancer patients first present with metastases where the location of the primary is unidentified; these are difficult to treat. In this study, using machine learning, the authors develop a method to determine the tissue of origin of a cancer based on whole sequencing data.
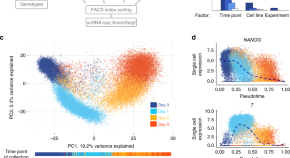
Studying the genetic effects on early stages of human development is challenging due to a scarcity of biological material. Here, the authors utilise induced pluripotent stem cells from 125 donors to track gene expression changes and expression quantitative trait loci at single cell resolution during in vitro endoderm differentiation.
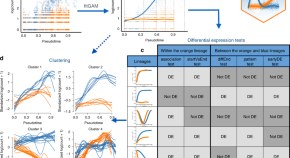
Downstream of trajectory inference for cell lineages based on scRNA-seq data, differential expression analysis yields insight into biological processes. Here, Van den Berge et al. develop tradeSeq, a framework for the inference of within and between-lineage differential expression, based on negative binomial generalized additive models.
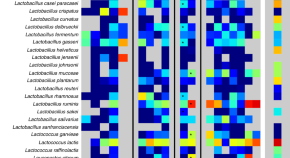
Here, Pasolli et al. perform a large-scale genome-wide comparative analysis of publicly available and newly sequenced food and human metagenomes to investigate the prevalence and diversity of lactic acid bacteria (LAB), indicating food as a major source of LAB species in the human gut.
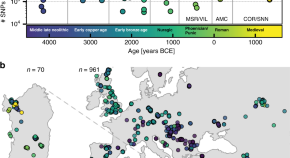
Ancient DNA analysis of early European farmers has found a high level of genetic affinity with present-day Sardinians. Here, the authors generate genome-wide capture data for 70 individuals from Sardinia spanning the Middle Neolithic to Medieval period to reveal relationships with mainland European populations shifting over time.
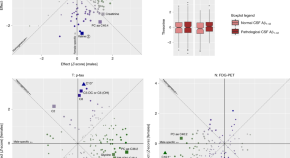
Sex and the APOE ε4 genotype are important risk factors for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. In the current study, the authors investigate how sex and APOE ε4 genotype modify the association between Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers and metabolites in serum.
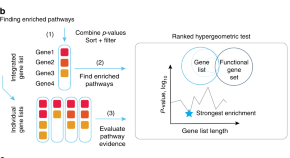
Multi-omics datasets pose major challenges to data interpretation and hypothesis generation owing to their high-dimensional molecular profiles. Here, the authors develop ActivePathways method, which uses data fusion techniques for integrative pathway analysis of multi-omics data and candidate gene discovery.
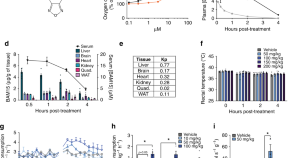
Obesity is a global pandemic with limited treatment options. Here, the authors show evidence in mice that the mitochondrial uncoupler BAM15 effectively induces fat loss without affecting food intake or compromising lean body mass.
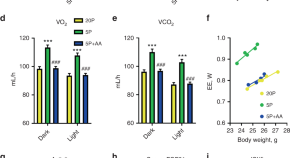
Dietary protein dilution, where protein is reduced and replaced by other nutrient sources without caloric restriction, promotes metabolic health via the hepatokine Fgf21. Here, the authors show that essential amino acids threonine and tryptophan are necessary and sufficient to induce these effects.
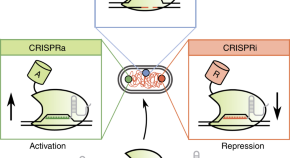
Multiplexed CRISPR technologies have recently emerged as powerful approaches for genetic editing and transcriptional regulation. Here the authors review this emerging technology and discuss challenges and considerations for future studies.
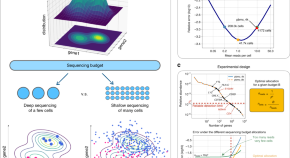
For single-cell RNA-seq experiments the sequencing budget is limited, and how it should be optimally allocated to maximize information is not clear. Here the authors develop a mathematical framework to show that, for estimating many gene properties, the optimal allocation is to sequence at the depth of one read per cell per gene.
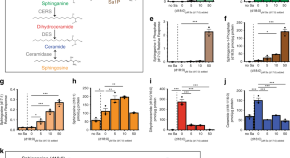
Ceramides are a type of sphingolipid (SL) that have been shown to play a role in several metabolic disorders. Here, the authors investigate the effect of SL-production by gut Bacteroides on host SL homeostasis and show that microbiome-derived SLs enter host circulation and alter ceramide production.

European populations underwent strong genetic changes during the Neolithic. Here, Furtwängler et al. provide ancient nuclear and mitochondrial genomic data from the region of Switzerland during the end of the Neolithic and the Early Bronze Age that reveal a complex genetic turnover during the arrival of steppe ancestry.
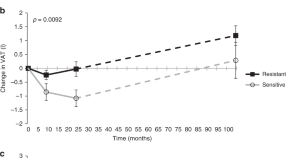
Brain insulin action regulates eating behavior and whole-body energy fluxes, however the impact of brain insulin resistance on long-term weight and body fat composition is unknown. Here, the authors show that high brain insulin sensitivity is linked to weight loss during lifestyle intervention and associates with a favorable body fat distribution.
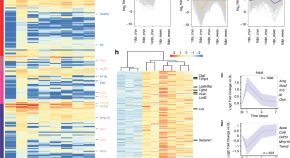
Macrophages mediate the fibrotic response after a heart attack by extracellular matrix turnover and cardiac fibroblasts activation. Here the authors identify an evolutionarily-conserved function of macrophages that contributes directly to the forming post-injury scar through cell-autonomous deposition of collagen.
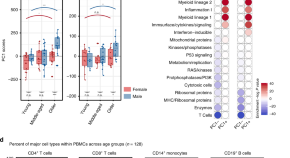
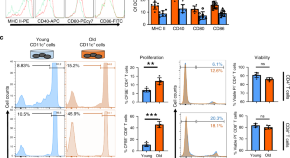
Whether the immune system aging differs between men and women is barely known. Here the authors characterize gene expression, chromatin state and immune subset composition in the blood of healthy humans 22 to 93 years of age, uncovering shared as well as sex-unique alterations, and create a web resource to interactively explore the data.
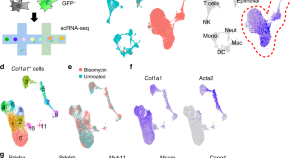
Collagen production by lung cells is critical to maintain organ architecture but can also drive pathological scarring. Here the authors perform single cell RNA sequencing of collagen-producing lung cells identifying a subset of pathologic fibroblasts characterized by Cthrc1 expression which are concentrated within fibroblastic foci in fibrotic lungs and show a pro-fibrotic phenotype.
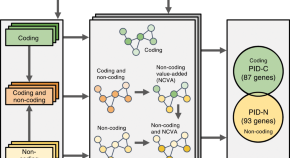
Understanding deregulation of biological pathways in cancer can provide insight into disease etiology and potential therapies. Here, as part of the PanCancer Analysis of Whole Genomes (PCAWG) consortium, the authors present pathway and network analysis of 2583 whole cancer genomes from 27 tumour types.
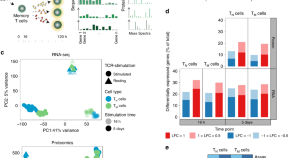
Cytokines critically control the differentiation and functions of activated naïve and memory T cells. Here the authors show, using multi-omics and single-cell analyses, that naïve and memory T cells exhibit distinct cytokine responses, in which an ‘effectorness gradient’ is depicted by a transcriptional continuum, which shapes the downstream genetic programs.